What is Acne?
Acne is also commonly called as zits or pimples. They are one of the most common skin problems in adolescents as well as adults. Acne refers to an inflammatory disorder of the skin when the secretion of sebaceous glands- known as sebum- along with dead cells gets trapped inside the skin. Bacteria may grow in these entrapments and lead to the formation of pus, triggering more severe Acne.
What are the types of Acne?
Acne may manifest in different forms based on its appearance and underlying causes.
- Whiteheads These are white bumps on the skin that are caused by sebum-plugged hair follicles beneath the skin.
- Blackheads When the plugged follicles reach the outer layer of skin and open up, the white content (sebum) gets exposed to air and discolours, leading to black bumps on the skin surface; these are called as blackheads.
- Papules These are small bumps, usually pink or reddish coloured, which are painful to touch. They are inflamed lesions, and the patient should avoid touching them repeatedly with a hand or finger.
- Pustules or pimples These are the typical white or yellow pus-filled bumps that may have an inflamed or red base.
- Nodules This refers to lesions that are painful, solid and larger in size and are lodged deep in the skin. They can become pus-filled or spread wide across (cystic Acne).
What causes Acne?
The most basic cause of Acne is excess or high production of oil in the pores of the skin and clogging of dead skin cells in the pore. These two can lead to bacterial growth and pus formation subsequently.
The following factors may increase the risk for Acne
| Hormones |
Elevated levels of androgens, the male sex hormones, can contribute to the development of Acne by stimulating the enlargement of sebaceous glands and increasing sebum production. Hormonal fluctuations in pregnancy can also lead to Acne. |
| Family history | Hereditary role cannot be ruled out, and children are more likely to get Acne if their parents suffer from Acne. |
| Medications | Hormonal supplements, Steroids and Lithium-containing medicines can exacerbate Acne. |
| Diet | Junk food can worsen Acne. |
| Stress | Though stress may not cause Acne directly, it can exacerbate Acne. |
| Environmental irritants | Severe humidity, pollution, etc., can make Acne worse. |
| Physical scrubs | Scrubbing your skin too hard leads to damage to natural barriers and may increase sebum production, leading to clogging of pores and Acne. |
Myths and Facts about Acne
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| Acne happens only in adolescents and teens | NO! Acne is more common in teens and adolescents but can occur in adults with the same or more intensity. |
| Acne will not leave scars if popped | NO! Never pop your Acne as that will lead to scarring and discolouration of the skin and may lead to further spread of infection. |
| Acne can be treated with Toothpaste | NO! Toothpastes are great-FOR YOUR TEETH, not your skin! Not only can Toothpaste make your Acne and skin more irritated, inflamed and red, but it also leads to a much worse looking scar in the long run. There are much better over-the-counter products for managing Acne. Consult your doctor about them for better results. |
| Acne is caused by dirt | NO. Acne is caused due to plugging of sebum under the skin in follicles. Dirt, however, can lead to infection/bacteria entering your Acne and cause flaring up of existing Acne. |
| Acne occurs only on the face | NO! Acne can happen across the body wherever sebum-producing glands are present, e.g., back, buttocks, shoulders, etc. All forms of Acne are treatable |
| Getting facials regularly will clear the skin of Acne | Facials include massage of the skin with oils and creams, followed by using masks. The massage will activate the oil glands to emit more oil, prompting more Acne. |
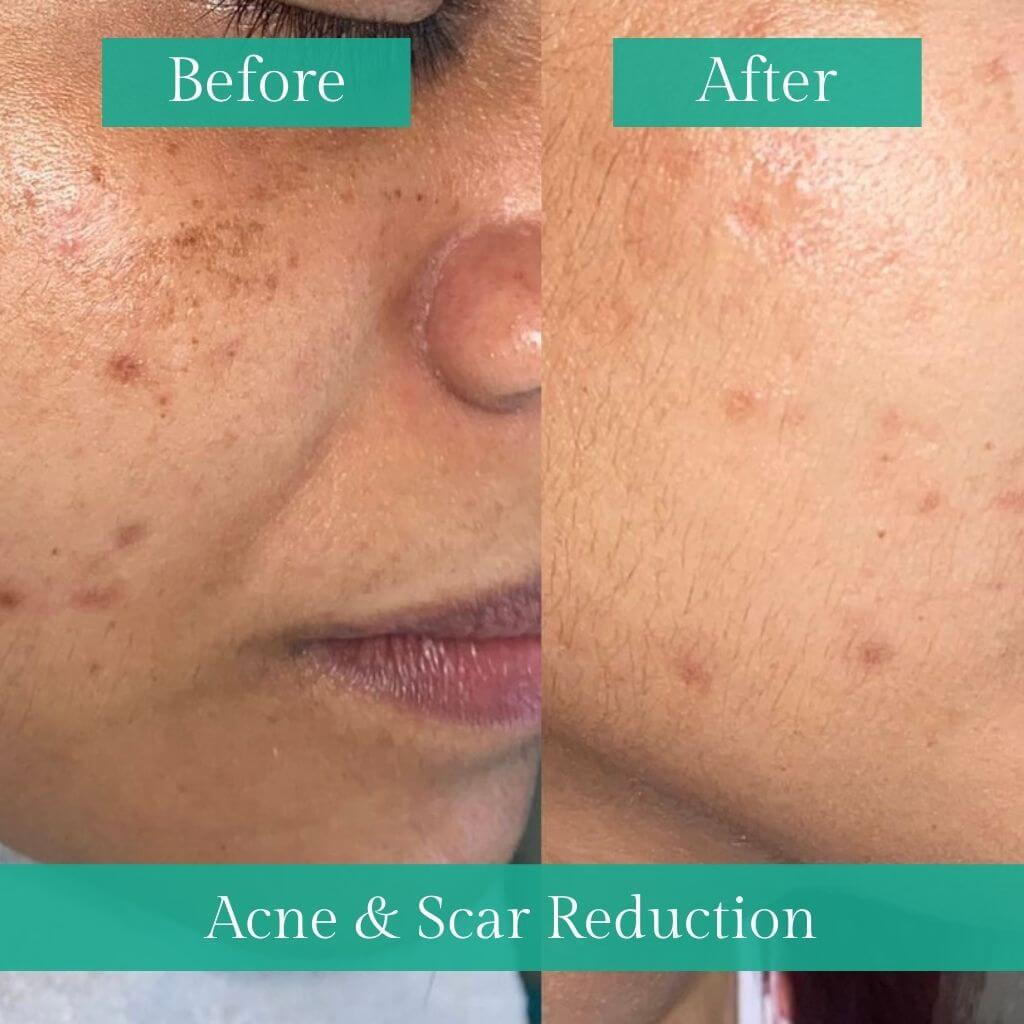
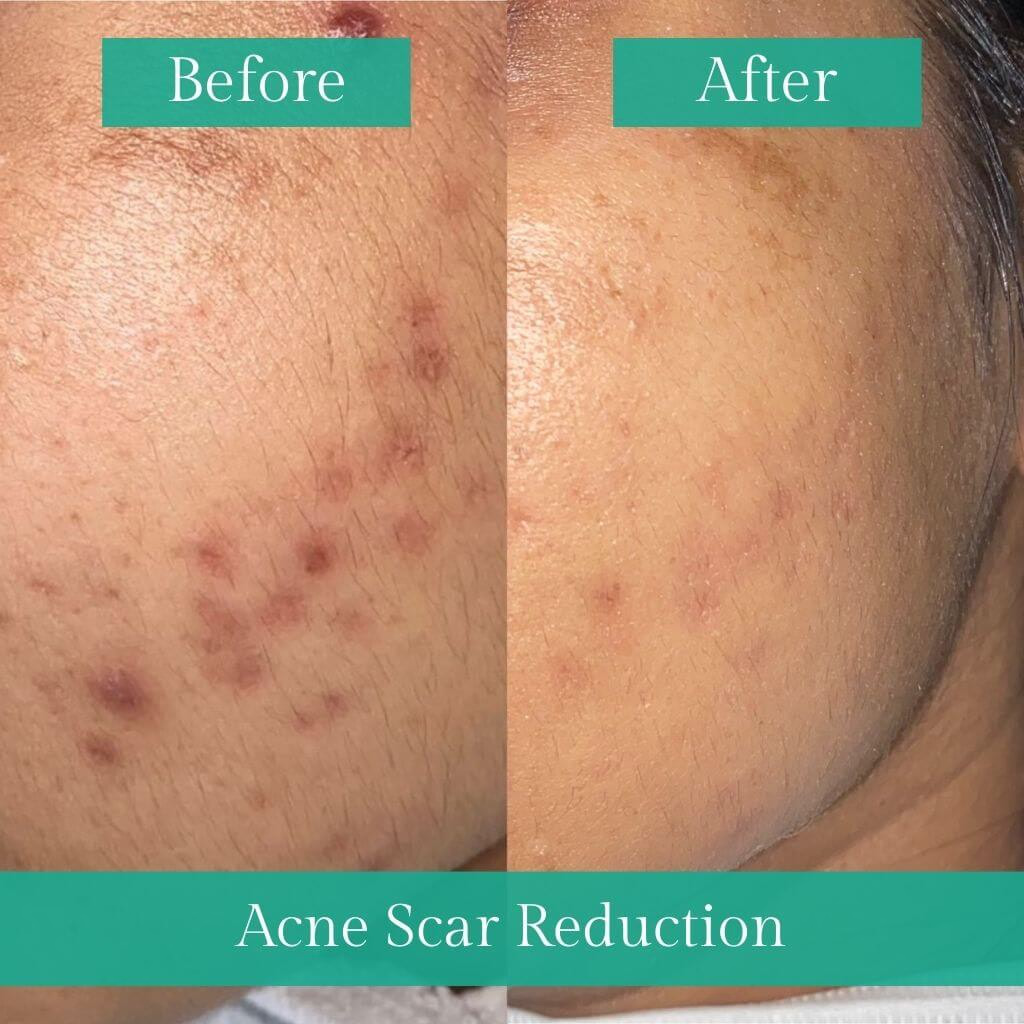
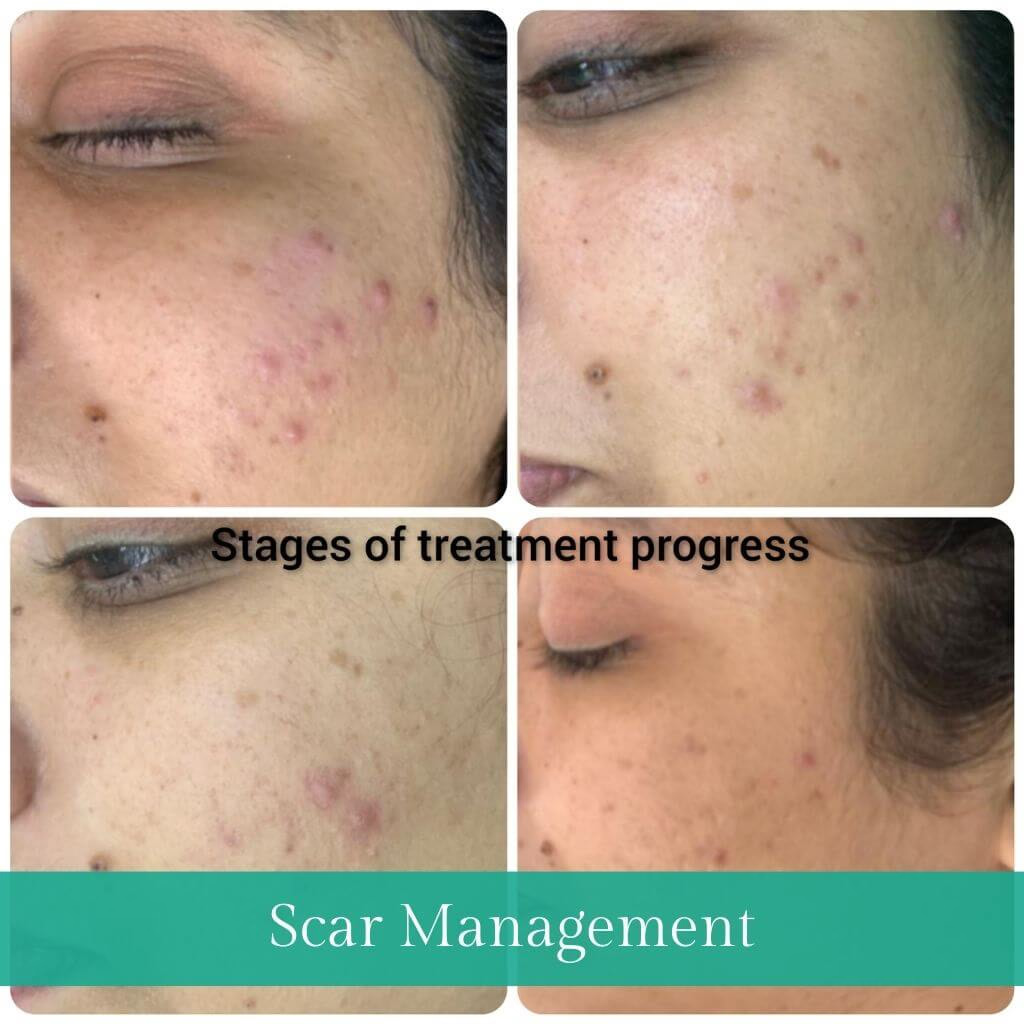
How can Acne and scars of Acne be treated?
Treatment of Acne depends on the doctor diagnosing the type of Acne you have. The following are some of the lines of treatment beneficial for the management of facial Acne and acne scars.
Medication
- Acne medications function by either diminishing oil production and inflammation or by addressing bacterial infections.
- Depending on your age the type and severity of your Acne, your doctor will formulate a regimen for you.
- Topical medications ( such as retinoid antibiotics like clindamycin with benzoyl peroxide) and azelaic and salicylic acid are often used in combination with drugs you take by mouth (oral medication).
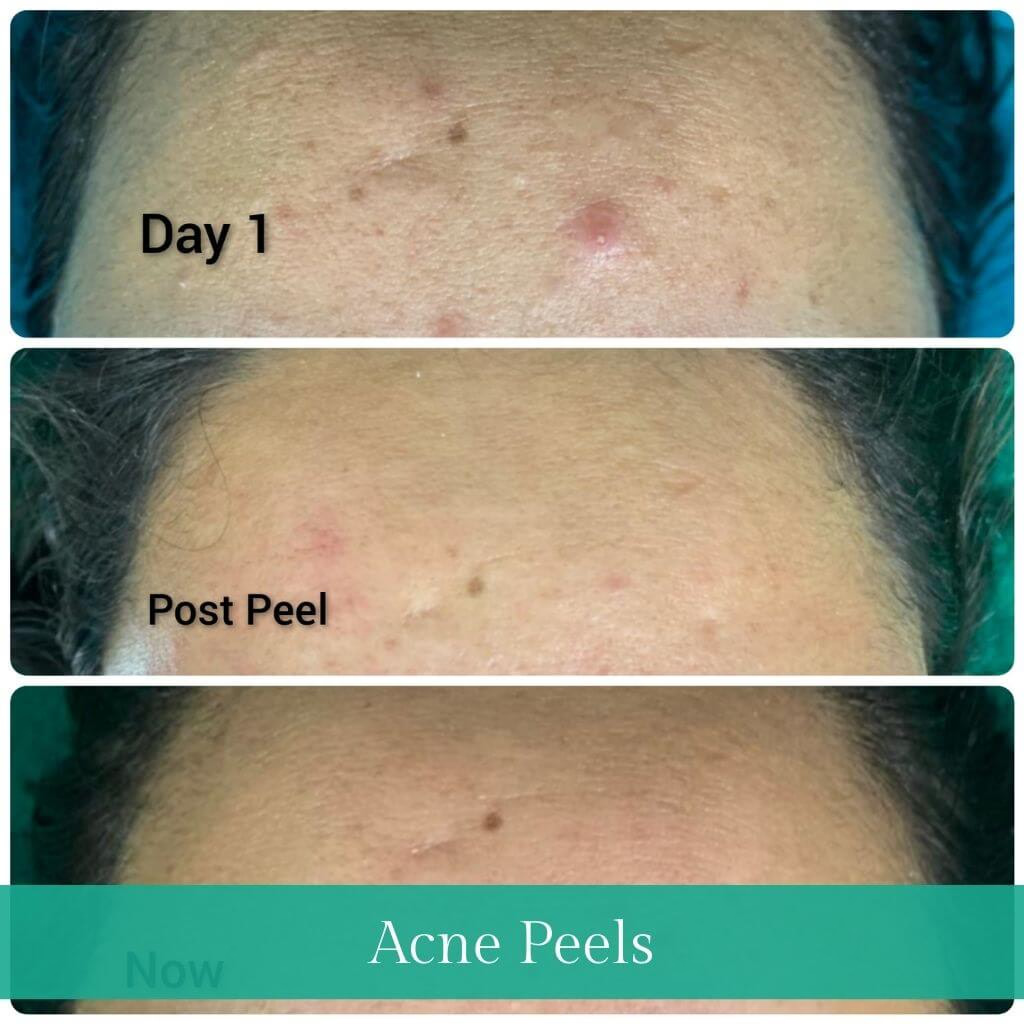
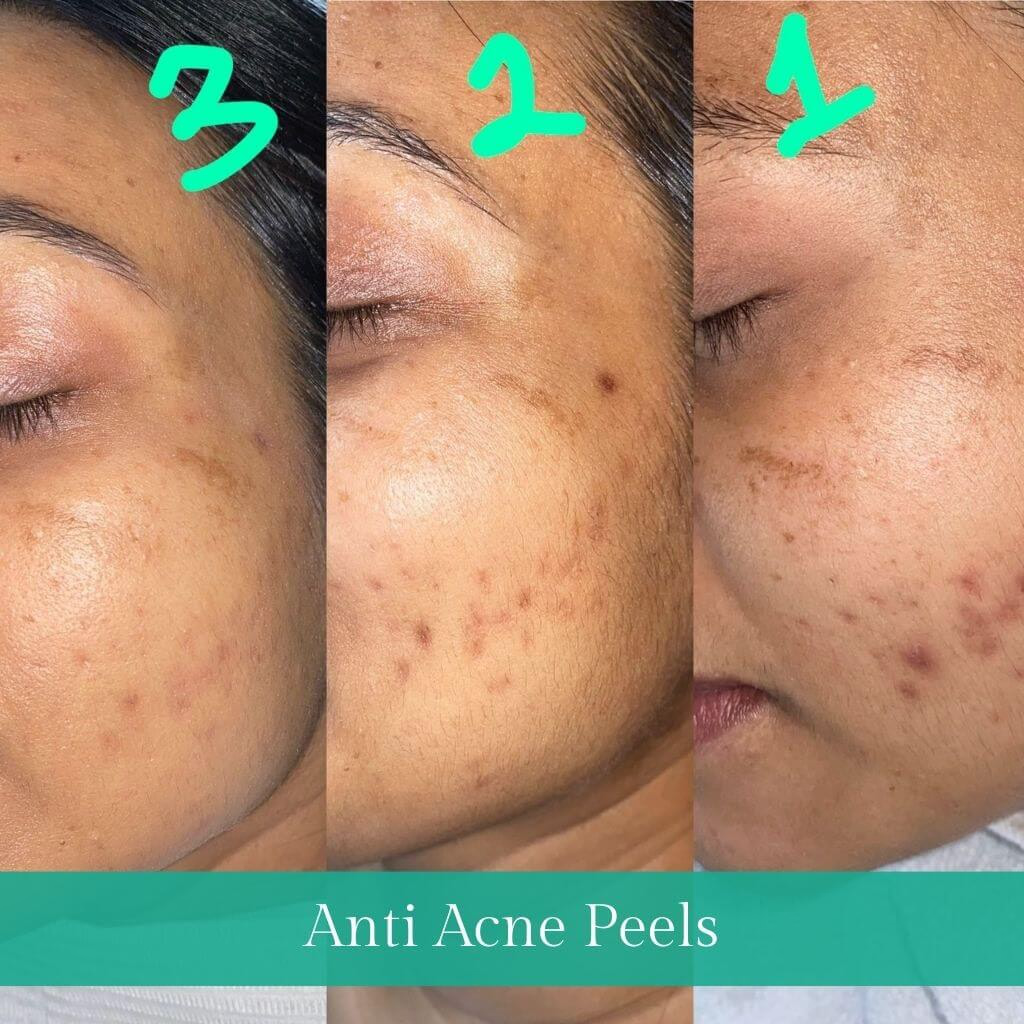
Chemical peels
- This procedure uses chemical solutions, such as salicylic acid, glycolic acid or retinoic acid, for topical management of Acne. It improves the appearance of the skin, reduction of Acne and also lightens acne scars and marks.
Dermabrasion
- During the procedure, a doctor guides a small motorized device over the skin with steady, gentle pressure. This device is equipped with an abrasive wheel or brush at its tip, which effectively eliminates the outer layers of the skin.
Microneedling & PRP
- This process involves the application of an anaesthetic to numb the skin and piercing with fine microneedles and depositing platelet-rich plasma (fractionated from blood using a special centrifuge) rich in growth and repair factors to improve skin quality texture and reduce blemishes and scars. It also stimulates collagen formation in the underlying tissue. It is one of the safest and most effective ways to manage acne scars, and results come in 2-5 sittings depending on the severity of the problem.
Laser resurfacing.
- Laser treatments are gaining popularity in the management of acne scars due to their high efficacy, although individuals with darker skin or a keloid history face an elevated risk of side effects.